Today’s digital-driven business landscape ensures that enterprises are constantly seeking innovative solutions to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and drive sustainable growth. At the forefront of this transformation stands SAP Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) – a comprehensive software suite that has been redefining the way organizations manage their core business processes.
SAP ERP is more than just a technology; it’s a strategic enabler that empowers businesses to navigate the complexities of the modern market and stay ahead of the competition. By integrating critical functions such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer relationship management, SAP ERP provides a unified platform for seamless data flow and informed decision-making.
In this in-depth exploration, we’ll delve into the transformative power of SAP ERP, uncovering its key features, implementation strategies, and the tangible benefits it can deliver to organizations of all sizes. Whether you’re a seasoned SAP user or exploring the potential of ERP for the first time, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to harness the full potential of this game-changing technology.
Understanding the Foundations of SAP Enterprise Resource Planning
SAP ERP, short for SAP Enterprise Resource Planning, is a comprehensive software suite developed by the German multinational corporation, SAP SE. Launched in 1972, SAP ERP has evolved over the decades to become a market-leading solution, trusted by organizations across a wide range of industries.
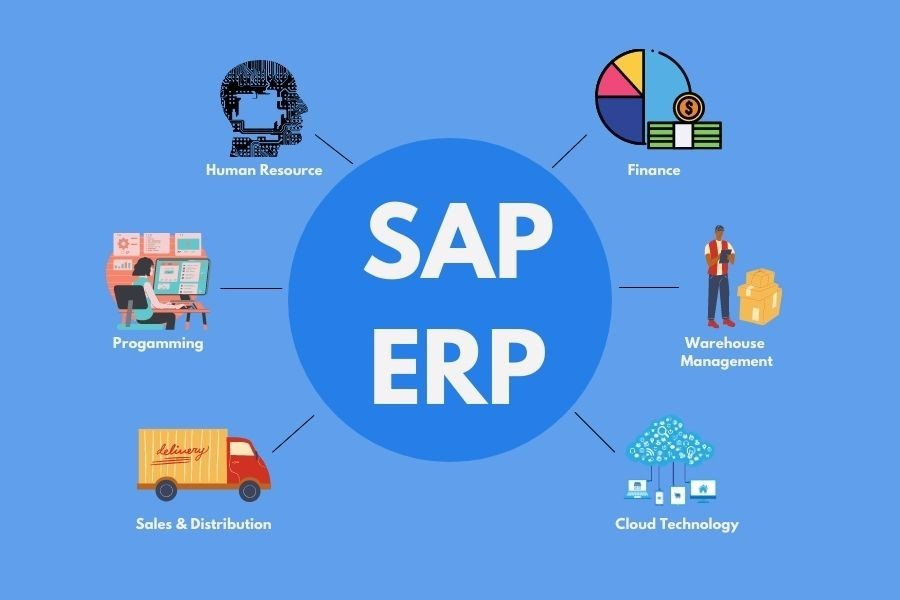
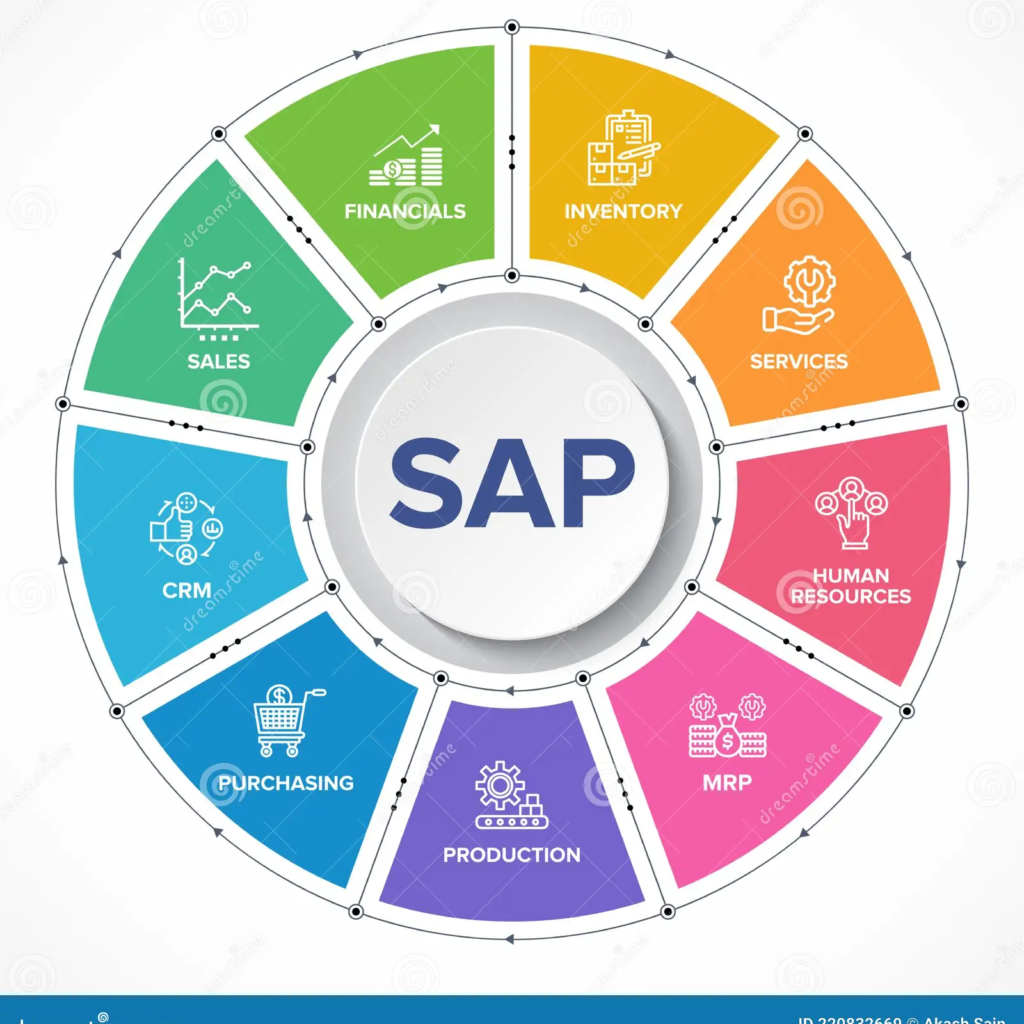
At its core, SAP ERP is designed to integrate and streamline an organization’s core business processes, enabling real-time data access, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced decision-making capabilities. The software encompasses a diverse range of modules, each tailored to address specific functional areas, including:
Financial Management (FI)
- General Ledger Accounting
- Accounts Payable and Receivable
- Asset Accounting
- Controlling (CO)
Human Capital Management (HCM)
- Personnel Administration
- Payroll
- Time Management
- Talent Management
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
- Materials Management (MM)
- Production Planning (PP)
- Sales and Distribution (SD)
- Logistics Execution (LE)
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Sales
- Service
- Marketing
Additional Modules
- Project System (PS)
- Plant Maintenance (PM)
- Quality Management (QM)
- Business Intelligence (BI)
The modular design of SAP ERP allows organizations to implement the specific functionalities they require, ensuring a tailored solution that aligns with their unique business needs. This flexibility enables enterprises to streamline their operations, improve data integration, and enhance overall efficiency.

The Evolution of SAP Enterprise Resource Planning: From R/3 to S/4HANA
The journey of SAP Enterprise Resource Planning has been marked by continuous innovation and adaptation to the changing business landscape. The software’s evolution can be traced through the following key milestones:
SAP R/3 (1992-2004)
The original SAP ERP system, known as SAP R/3, was launched in 1992 and quickly gained widespread adoption. R/3 was built on a client-server architecture, providing organizations with a comprehensive suite of integrated business applications.
SAP ERP (2004-2015)
In 2004, SAP introduced a new version of its ERP system, known as SAP ERP or SAP ECC (ERP Central Component). This iteration incorporated enhanced functionality, improved user experience, and better integration with other SAP solutions, such as the SAP Business Warehouse and SAP Strategic Enterprise Management.
SAP S/4HANA (2015-Present)
The latest and most advanced version of SAP ERP is SAP S/4HANA, introduced in 2015. Leveraging the power of in-memory computing and the SAP HANA database, S/4HANA offers a simplified data model, real-time analytics, and intelligent automation capabilities, enabling organizations to make faster, more informed decisions.
The transition from SAP R/3 to SAP S/4HANA has been a significant milestone in the evolution of the ERP system. S/4HANA not only provides enhanced functionality but also lays the foundation for businesses to embrace the digital transformation and harness the power of emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT).

Key Features and Capabilities of SAP Enterprise Resource Planning
SAP Enterprise Resource Planning is renowned for its comprehensive suite of features and capabilities that cater to the diverse needs of modern enterprises. Let’s explore some of the key functionalities that make SAP ERP a game-changer in the ERP landscape:
Integrated Business Processes
SAP ERP seamlessly integrates an organization’s core business processes, including finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer relationship management, into a single, cohesive system. This integration ensures data consistency, streamlined workflows, and real-time visibility across the entire enterprise.
Real-Time Data and Analytics
The in-memory computing capabilities of SAP S/4HANA enable organizations to access and analyze data in real-time, empowering them to make informed, data-driven decisions. Advanced analytics and reporting tools provide valuable insights, allowing businesses to identify trends, optimize operations, and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Intelligent Automation
SAP ERP leverages intelligent automation and machine learning to streamline repetitive tasks, reduce manual errors, and enhance overall efficiency. From automated invoice processing to predictive maintenance, these capabilities help organizations operate more efficiently and focus on strategic priorities.
Focusing on Scalability and Mobility
Scalability and Flexibility
SAP ERP is designed to accommodate the evolving needs of businesses, offering scalable solutions that can grow alongside an organization. The modular architecture allows enterprises to implement specific functionalities as required, ensuring a tailored solution that adapts to changing market conditions and business requirements.
Mobility and Collaboration
SAP ERP seamlessly integrates with mobile devices and collaboration platforms, enabling employees to access critical information, approve transactions, and collaborate in real-time, regardless of their location. This enhances productivity, decision-making, and overall business agility.
Industry-Specific Solutions
SAP ERP offers industry-specific solutions, catering to the unique needs of various sectors, such as manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and public sector. These pre-configured solutions accelerate implementation, reduce customization efforts, and ensure best-practice business processes.
Compliance and Security
SAP ERP prioritizes data security and regulatory compliance, providing robust access controls, audit trails, and built-in support for industry-specific regulations. This ensures that organizations can operate with confidence, mitigating risks and maintaining the integrity of their data.
By leveraging these powerful features, organizations can streamline their operations, enhance decision-making, and drive sustainable growth, ultimately positioning themselves for long-term success in the ever-evolving business landscape.
Implementing SAP Enterprise Resource Planning: A Phased Approach
Implementing SAP Enterprise Resource Planning is a strategic and complex undertaking, requiring a well-planned approach to ensure a successful deployment. The implementation process typically follows a phased methodology, consisting of the following key stages:
Phase 1: Project Preparation
This initial phase involves defining the project scope, assembling the implementation team, and establishing a clear governance structure. During this phase, organizations also conduct a thorough assessment of their current business processes and IT infrastructure to identify areas for improvement.
Phase 2: Business Blueprint
In the business blueprint phase, the implementation team works closely with key stakeholders to document the organization’s business requirements, map existing processes, and design the future state of the SAP ERP system. This phase is crucial for ensuring that the solution aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Phase 3: Realization
The realization phase focuses on the actual configuration and customization of the SAP ERP system. This includes setting up the necessary modules, integrating with other systems, and testing the solution to ensure it meets the defined requirements.
Finally…
Phase 4: Final Preparation
During the final preparation phase, the implementation team conducts comprehensive testing, trains end-users, and prepares the organization for the go-live transition. This phase also involves finalizing data migration, cut-over planning, and the development of support and maintenance strategies.
Phase 5: Go-Live and Support
The final phase involves the actual go-live of the SAP ERP system, where the organization transitions from the legacy system to the new solution. This phase also includes ongoing support, user assistance, and continuous improvement initiatives to ensure the system’s long-term success.
Throughout the implementation process, effective change management, stakeholder engagement, and project governance are crucial for ensuring a smooth transition and maximizing the benefits of the SAP ERP system.

The Benefits of Implementing SAP ERP
Implementing SAP ERP can unlock a wide range of benefits for organizations, transforming their operations and positioning them for long-term success. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of adopting SAP ERP:
Improved Operational Efficiency
By integrating and streamlining core business processes, SAP ERP helps organizations eliminate data silos, reduce manual errors, and automate repetitive tasks. This leads to increased productivity, faster decision-making, and enhanced overall operational efficiency.
Enhanced Financial Management
SAP ERP’s robust financial management capabilities, including general ledger, accounts payable and receivable, and asset accounting, provide organizations with real-time visibility into their financial performance. This enables better financial planning, forecasting, and compliance management.
Strengthened Supply Chain Optimization
SAP ERP’s supply chain management module, which includes materials management, production planning, and logistics execution, helps organizations optimize their supply chain operations. This results in improved inventory management, reduced lead times, and enhanced customer service.
Focusing on CRM, Data Analytics and Compliance
Improved Customer Relationship Management
The CRM module within SAP ERP enables organizations to better understand and serve their customers. By integrating sales, service, and marketing functions, businesses can enhance customer engagement, improve responsiveness, and drive customer loyalty.
Increased Data Visibility and Analytics
The real-time data and advanced analytics capabilities of SAP ERP empower organizations to make informed, data-driven decisions. This leads to improved forecasting, better risk management, and the ability to identify and capitalize on new opportunities.
Enhanced Compliance and Security
SAP ERP’s robust security features and built-in support for regulatory compliance help organizations mitigate risks, protect sensitive data, and maintain the integrity of their operations, even in highly regulated industries.
Scalability and Adaptability
The modular design of SAP ERP allows organizations to scale their solution as their business grows, while also adapting to changing market conditions and evolving business requirements. This ensures that the ERP system remains a strategic enabler for long-term success.By leveraging these benefits, organizations can achieve a competitive edge, improve their bottom line, and position themselves for sustainable growth in the ever-evolving business landscape.
Overcoming Challenges in SAP ERP Implementation
While the benefits of implementing SAP Enterprise Resource Planning are substantial, the process is not without its challenges. Organizations must be prepared to navigate various obstacles to ensure a successful deployment and long-term adoption of the system. Some of the key challenges include:
Complexity and Customization
SAP ERP is a highly complex system, with a vast array of functionalities and configurations. Striking the right balance between standardization and customization to meet specific business requirements can be a significant challenge, often requiring extensive planning and change management.
Data Migration and Integration
Migrating data from legacy systems to the SAP ERP platform and ensuring seamless integration with other critical business applications can be a time-consuming and technically demanding process. Careful planning and execution are essential to maintain data integrity and minimize disruptions.
Change Management
Implementing a new ERP system often requires significant changes to an organization’s processes, workflows, and user roles. Effective change management, including comprehensive training and user adoption strategies, is crucial for ensuring a smooth transition and minimizing resistance to the new system.
Talent and Skill Gaps
Implementing and maintaining an SAP ERP system requires specialized technical and functional skills. Organizations may face challenges in recruiting and retaining the necessary talent, which can impact the success of the implementation and ongoing system support.
Budgeting and Cost Control
SAP ERP implementation can be a significant investment, with costs ranging from software licenses and hardware to consulting services and ongoing maintenance. Careful budgeting, cost control, and return on investment (ROI) analysis are essential to ensure the project’s financial viability.
Organizational Alignment
Successful SAP ERP implementation requires alignment across the organization, from executive sponsorship to end-user buy-in. Ensuring that the project’s objectives and benefits are clearly communicated and understood can be a critical success factor.
To overcome these challenges, organizations should adopt a comprehensive change management strategy, invest in employee training and development, and establish robust project governance and risk management practices. By addressing these challenges proactively, businesses can maximize the value of their SAP ERP investment and position themselves for long-term success.
SAP ERP Implementation: Industry Insights and Case Studies
To better understand the real-world impact of SAP Enterprise Resource Planning, let’s explore some industry-specific case studies and insights:
Manufacturing
Siemens, a global industrial conglomerate, implemented SAP S/4HANA to streamline its manufacturing operations, enhance supply chain visibility, and improve decision-making. The implementation resulted in a 30% reduction in inventory levels and a 20% increase in on-time delivery performance.
Retail
Adidas, the renowned sportswear brand, leveraged SAP ERP to unify its global operations, improve inventory management, and enhance customer experience. The implementation enabled Adidas to achieve a 15% reduction in inventory costs and a 20% increase in online sales.
Healthcare
Novartis, a leading pharmaceutical company, adopted SAP ERP to integrate its finance, supply chain, and R&D functions. The implementation helped Novartis achieve a 25% reduction in cycle time for new product launches and a 35% improvement in forecast accuracy.
Public Sector
The City of Los Angeles implemented SAP ERP to modernize its financial management, human resources, and procurement processes. The project resulted in a 20% reduction in processing time for vendor payments and a 15% increase in employee productivity.
Energy
Enel, a multinational energy company, deployed SAP S/4HANA to streamline its global operations, enhance data analytics, and drive sustainability initiatives. The implementation enabled Enel to achieve a 10% reduction in operational costs and a 15% improvement in asset utilization.
These case studies demonstrate the transformative impact of SAP ERP across various industries, highlighting the tangible benefits organizations can achieve in terms of operational efficiency, financial performance, and strategic decision-making.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future with SAP ERP
In the ever-evolving business landscape, organizations are constantly seeking innovative solutions to drive efficiency, enhance competitiveness, and position themselves for long-term success. SAP ERP has emerged as a game-changing technology, offering a comprehensive and integrated platform that can revolutionize the way businesses operate.
By leveraging the power of SAP ERP, enterprises can unlock a wealth of benefits, from improved operational efficiency and enhanced financial management to strengthened supply chain optimization and better customer relationship management. The system’s scalability, adaptability, and industry-specific solutions ensure that organizations can tailor the ERP system to their unique needs, positioning them for sustained growth and success.
While the implementation of SAP ERP is not without its challenges, a well-planned and executed strategy, coupled with effective change management and talent development, can help organizations overcome these obstacles and reap the full rewards of this transformative technology.
In Summary…
As businesses continue to navigate the complexities of the digital age, the adoption of SAP ERP will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of enterprise operations. By embracing this powerful solution, organizations can unlock new levels of efficiency, agility, and innovation, ultimately positioning themselves as leaders in their respective industries.
Don’t forget to subscribe to Shift Gear X for more articles. Need expert advice or consulting? Be sure to visit Shift Gear.
Check this also – Calling All Caregivers! DXC Technology Tackles Parkinson’s! – Tech News Before It’s News | Shift GearX
You will also love – Moving SAP Transport Request to Different Server: A Step-by-Step Guide – Tech News Before It’s News | Shift GearX
Aldo Read: Top 10 Warehouse Management Systems: Your Complete Guide – Tech News Before It’s News | Shift GearX