Today, effective supplier relationship management (SRM) has become a critical component of success for organizations across industries. As supply chains grow increasingly complex and global, the ability to cultivate strong, collaborative partnerships with suppliers is no longer a luxury, but a necessity.
SRM is about more than just managing costs and ensuring timely deliveries. It’s about fostering a culture of trust, communication, and mutual benefit that allows both parties to thrive. By investing in SRM, businesses can unlock a host of benefits, from reduced risks and improved quality to enhanced innovation and greater agility in the face of disruption.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the key principles of SRM, share best practices and expert tips, and provide you with the tools and strategies you need to take your supplier relationships to the next level. Whether you’re a seasoned procurement professional or just starting out, this article is your roadmap to success in the dynamic world of supplier relationship management.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Supplier Relationship Management
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of SRM, let’s take a step back and examine the core principles that underpin this critical business function.
What is Supplier Relationship Management?
Supplier relationship management is a strategic approach to managing an organization’s interactions with the suppliers that provide the goods and services it needs to operate effectively. It involves a range of activities, from supplier selection and contract negotiation to performance monitoring and continuous improvement.
At its heart, SRM is about building strong, collaborative relationships with suppliers that are mutually beneficial and aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives. By fostering a culture of trust, communication, and shared goals, businesses can unlock a host of benefits, from reduced costs and improved quality to enhanced innovation and greater resilience in the face of disruption.

The Evolution of Supplier Relationship Management
While the concept of SRM has been around for decades, it has evolved significantly in recent years in response to changing market dynamics and technological advancements. In the past, supplier relationships were often transactional in nature, with a focus on cost reduction and short-term performance metrics.
Today, however, the focus has shifted towards a more strategic, long-term approach that emphasizes collaboration, innovation, and mutual value creation. As supply chains have become more complex and global, businesses have recognized the need to work more closely with their suppliers to navigate these challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
The Benefits of Effective Supplier Relationship Management
Investing in effective SRM can yield a host of benefits for organizations, including:
- Reduced costs and improved profitability
- Enhanced quality and reliability of goods and services
- Improved responsiveness to changing market conditions
- Increased innovation and access to new technologies
- Greater resilience in the face of supply chain disruptions
- Stronger brand reputation and customer loyalty
By cultivating strong, collaborative relationships with suppliers, businesses can create a competitive advantage that sets them apart in today’s dynamic marketplace.
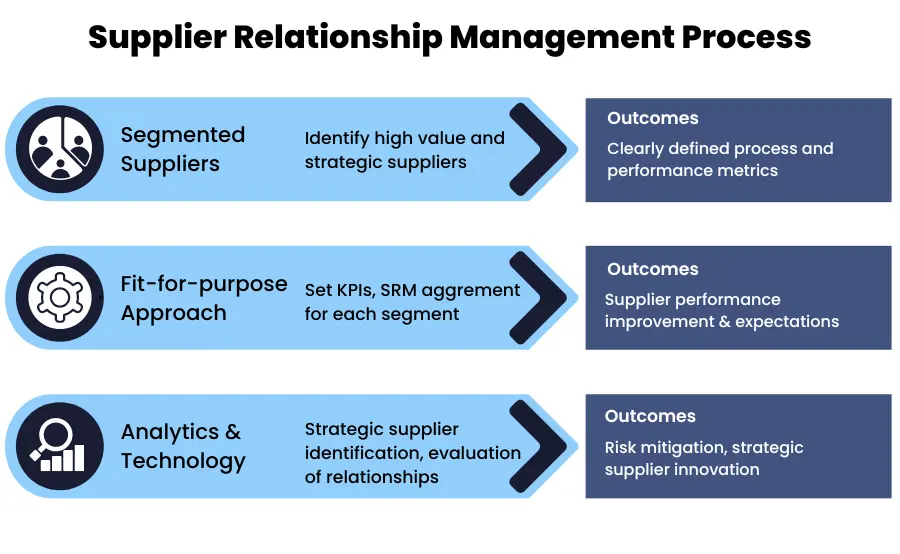
Developing a Robust Supplier Relationship Management Strategy
Now that we’ve established the fundamentals of SRM, let’s dive into the process of developing a robust strategy that aligns with your organization’s unique needs and goals.
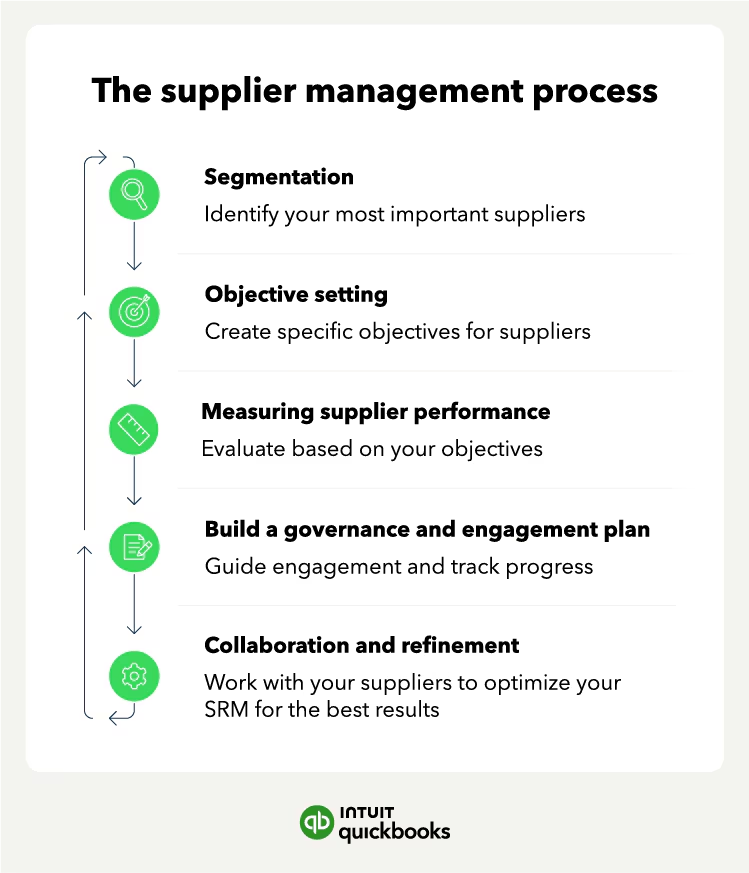
Step 1: Assess Your Current Supplier Relationships
The first step in developing an effective SRM strategy is to assess your current supplier relationships. This involves evaluating the performance, risk profile, and strategic alignment of each supplier, as well as identifying areas for improvement and potential opportunities for collaboration.
To conduct this assessment, you can use a variety of tools and techniques, such as supplier scorecards, risk matrices, and SWOT analyses. It’s also important to gather input from key stakeholders across the organization, including procurement, operations, and finance.
Step 2: Segment Your Supplier Base
Once you’ve assessed your current supplier relationships, the next step is to segment your supplier base based on factors such as strategic importance, spend, and risk. This will help you prioritize your efforts and allocate resources more effectively.
One common approach to supplier segmentation is the Kraljic matrix, which categorizes suppliers into four quadrants based on their profit impact and supply risk:
| Quadrant | Profit Impact | Supply Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Leverage | High | Low |
| Strategic | High | High |
| Bottleneck | Low | High |
| Noncritical | Low | Low |
By understanding where each supplier falls within this matrix, you can develop tailored strategies for managing and optimizing these relationships.
Step 3: Develop Supplier Relationship Management Plans
With your supplier base segmented, the next step is to develop SRM plans for each category of suppliers. These plans should outline the specific strategies, tactics, and performance metrics that will be used to manage and optimize these relationships.
For example, a strategic supplier relationship management plan might focus on:
- Establishing joint business objectives and aligning on key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Implementing collaborative planning and forecasting processes
- Investing in joint innovation and R&D initiatives
- Conducting regular performance reviews and continuous improvement activities
In contrast, a noncritical supplier relationship management plan might emphasize:
- Streamlining procurement processes and reducing transaction costs
- Implementing automated ordering and invoicing systems
- Conducting periodic performance reviews and spot audits
- Exploring opportunities for supplier consolidation or rationalization
By tailoring your SRM plans to the unique needs and characteristics of each supplier category, you can ensure that your efforts are focused on the areas that will yield the greatest impact.
Step 4: Implement and Monitor Your SRM Strategy
With your SRM plans in place, the next step is to implement and monitor your strategy. This involves:
- Communicating your SRM strategy and plans to suppliers and internal stakeholders
- Providing training and support to procurement and supply chain teams
- Implementing enabling technologies and systems, such as supplier portals and collaboration platforms
- Conducting regular performance reviews and adjusting your strategy as needed
To ensure the success of your SRM strategy, it’s important to establish clear roles and responsibilities, set measurable goals and KPIs, and regularly monitor and report on progress. This will help you identify areas for improvement, celebrate successes, and make data-driven decisions about how to optimize your supplier relationships over time.
Best Practices for Effective Supplier Relationship Management
As you implement your SRM strategy, it’s important to keep in mind a few key best practices that can help you drive success:
Foster a Culture of Trust and Collaboration
One of the most important factors in effective SRM is the ability to foster a culture of trust and collaboration between your organization and its suppliers. This involves:
- Communicating openly and honestly about goals, challenges, and expectations
- Demonstrating a genuine commitment to the success of your suppliers
- Investing in joint initiatives and shared learning opportunities
- Resolving conflicts and issues in a constructive and timely manner
By cultivating a culture of trust and collaboration, you can create an environment where both parties feel empowered to take risks, share ideas, and work together towards common goals.
Leverage Data and Analytics
In today’s data-driven business landscape, effective SRM requires the ability to leverage data and analytics to drive decision-making and continuous improvement. This involves:
- Collecting and analyzing performance data from across the supply chain
- Using predictive analytics to identify emerging risks and opportunities
- Implementing supplier scorecards and dashboards to track key metrics
- Conducting regular supplier audits and assessments
By harnessing the power of data and analytics, you can gain deeper insights into your supplier relationships, identify areas for improvement, and make more informed decisions about how to optimize these partnerships over time.
Invest in Supplier Development
Another key best practice in SRM is investing in supplier development initiatives that help your suppliers grow and improve their capabilities. This can include:
- Providing training and support in areas such as quality management, lean manufacturing, and sustainability
- Offering financial assistance or access to capital for strategic investments
- Sharing best practices and lessons learned from across your supplier base
- Recognizing and rewarding high-performing suppliers through awards and incentives
By investing in supplier development, you can help your suppliers become more capable, competitive, and aligned with your organization’s goals and values.
Embrace Continuous Improvement
Finally, effective SRM requires a commitment to continuous improvement that allows you to adapt and evolve your strategies and tactics in response to changing market conditions and emerging opportunities. This involves:
- Regularly reviewing and updating your SRM plans and processes
- Soliciting feedback from suppliers and internal stakeholders
- Conducting benchmarking and competitive analysis to identify best practices
- Experimenting with new technologies and approaches to drive innovation
By embracing a culture of continuous improvement, you can ensure that your SRM strategy remains relevant, effective, and aligned with the needs of your business and your suppliers.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Supplier Relationship Management
While effective SRM can yield significant benefits, it’s not without its challenges. Some of the most common challenges that organizations face in implementing and optimizing their SRM strategies include:
- Lack of executive buy-in and support
- Siloed organizational structures and lack of cross-functional collaboration
- Insufficient resources and budget for SRM initiatives
- Difficulty in measuring and demonstrating the value of SRM
- Resistance to change from suppliers or internal stakeholders
- Lack of data and analytics capabilities to support decision-making
To overcome these challenges, it’s important to:
- Build a strong business case for SRM and secure executive sponsorship
- Break down organizational silos and foster cross-functional collaboration
- Allocate sufficient resources and budget to support SRM initiatives
- Develop clear metrics and KPIs to measure the impact of SRM
- Communicate the benefits of SRM and engage suppliers and stakeholders in the process
- Invest in data and analytics capabilities to drive data-driven decision-making
By addressing these challenges head-on and taking a proactive, strategic approach to SRM, organizations can unlock the full potential of their supplier relationships and drive sustainable growth and success.
Conclusion
In today’s dynamic and interconnected business landscape, effective supplier relationship management has never been more important. By cultivating strong, collaborative relationships with suppliers, organizations can unlock a host of benefits, from reduced costs and improved quality to enhanced innovation and greater resilience in the face of disruption.
To succeed in SRM, it’s important to take a strategic, data-driven approach that aligns with your organization’s unique needs and goals. This involves assessing your current supplier relationships, segmenting your supplier base, developing tailored SRM plans, and implementing and monitoring your strategy over time.
By embracing best practices such as fostering a culture of trust and collaboration, leveraging data and analytics, investing in supplier development, and committing to continuous improvement, organizations can drive success in SRM and position themselves for long-term growth and success.
In Summary
Ultimately, effective SRM is not just about managing costs and ensuring timely deliveries – it’s about building a network of strategic partners who can help you navigate the challenges and capitalize on the opportunities of today’s fast-paced business world. By investing in SRM, organizations can create a competitive advantage that sets them apart in the marketplace and drives sustainable value for years to come.
Don’t forget to subscribe to Shift Gear X for more articles. Need expert advice or consulting? Be sure to visit Shift Gear.
Check this also – Uncovering the Complexities of ERP Requirements Management – Tech News Before It’s News | Shift GearX
You will also love – Moving SAP Transport Request to Different Server: A Step-by-Step Guide – Tech News Before It’s News | Shift GearX









